GROUP GOMEZ DE AGÜERO/ Project GO 3241 1-1
Dynamic and mechanisms of early life interactions between bacteriophage and its bacteria host in the skin
Staphylococcus epidermidis is one of the major human skin colonizers from birth. Although a beneficial member for setting up tissue homeostasis in early life, S. epidermidis is emerging as a life-threatening opportunistic pathogen causing neonatal sepsis. Whilst term infants house commensal strains, preterm infants harbor in their skin strains of S. epidermidis with pathogenic elements, high ability to form biofilms and antibiotic resistant cassettes. Naturally, intact skin prevents pathogen penetration, but it constitutes a stockage niche. Disruptions of skin integrity caused by i.e. indwelling catheters allows penetration of S. epidermidis into the blood leading to sepsis in the case of pathogenic strains.
The aim of the project is to investigate how phages could modulate the landscape of early life skin microbiota.
Our results will provide a framework for the development of target strategies to prevent skin accumulation of pathogenic Staphylococcus epidermidis and beyond that will lay the framework to modulate colonization by multidrug resistant bacteria.
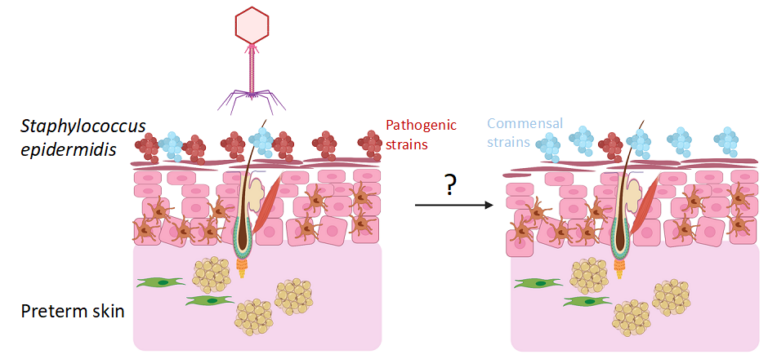
Created with biorender.
Principal Investigator
Dr. Mercedes Gomez de Agüero
Institute of Systems Immunology. Max-Planck Research Group.
Julius-Maximilians-University Würzburg
E-Mail: mercedes.gomez@uni-wuerzburg.de
Homepage: https://www.med.uni-wuerzburg.de/en/systemimmunologie/research/host-microbial-interactions-gomez-de-agueero-lab/
PostDoc
Dr. Aryan Rahimi Midani, (aryan.rahimi-midani@uni-wuerzburg.de)
Publications
- Shmeleva EV, Gomez de Agüero M, Wagner J, Enright AJ, Macpherson AJ, Ferguson BJ, Smith GL. Smallpox vaccination induces a substantial increase in commensal skin bacteria that promote pathology and enhance immunity. Plos Pathogens 2022, 18(4): e1009854. PMID: 35446919
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35446919/ - Feuerstein R, Forde AJ, Lohrmann F, Kolter J, Ramirez NJ, Zimmermann J, Gomez de Agüero M, Henneke P. Resident macrophages acquire innate immune memory in staphylococcal skin infection. eLife, 2020, 9:e55602. PMID: 32639232
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7343389/ - Gomez de Agüero M*, Ganal-Vonarburg S*, Fuhrer T, Rupp S, Uchimura Y, Li H, Steinert A, Heikenwalder M, Hapfelmeier S, Sauer U, McCoy KD*, Macperson AJ.* The maternal microbiota drives early postnatal innate immune development. (*Equal contribution). Science, 2016 March 18th, 351(6279):1296-302. PMID: 26989247